
When your engine cranks but no start. It usually means your engine is having trouble, producing a spark, getting fuel, or creating compression.
But, what if, ignition, fuel, and compression were all checked. and are all working good.
When your engine cranks but no start, it can be difficult to fix, if you don’t know where to begin troubleshooting.
So, what can you do, when your engine cranks but no start. It was easy to find the problem in the old days, when engines were very basic. In today’s vehicles there are tons of sensor, relays, modules and computers. Each one has to be working properly, and be able to do its job.
Many of these components talk to each other, sending information back and forth. So, if one fails it can affect others, making it even harder to find the real problem. And, sometimes your engine turns over, but just will not start.

Computers in modern vehicles monitor many of these components, and can set Trouble Codes when problems arise. So, your first check is to confirm any engine codes.
Faults in other systems, not just ignition, fuel, or compression problems, can stop your engine from starting. A system component itself may be faulty, or there may be a problem with it’s wire connector or harness.
Sometimes you will need to dig a little deeper, in your diagnostic testing to find the problem.
Things To Check That May Be Causing, Your Engine Cranks But No Start Problem:
Fuses And Relays
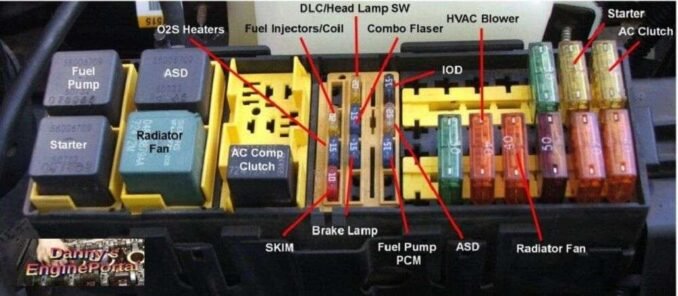
Checking fuses and relays is easy to do. And, can be done in just a few minutes, using a test light. Fuses and relays fatigue causing them to blow, which will cut electrical current to crucial components. It is also possible to cause a engine cranks but no start issue. So, the power center is located in the engine compartment. It is usually a large rectangular plastic box with a removable cover. If you can’t find it, refer to your vehicle owner’s manual for its location.
Alarm – Security System

When cranking the engine over, does the security light flash? Each manufacturer disables the engine in different ways when in security mode. Occasionally the system will become confused, due to a glitch or error. And, that means the alarm system must be reset. As a result, your engine cranks but no start.
(EGR) Valve

The (EGR) valve, introduces a measured amount of exhaust gases, into the intake manifold. And, the get burned for a second time. This helps lower engine temperature, and harmful emissions. But, the valve can fail and stick either open or closed. When the valve sticks open, it may prevent your engine from starting. Other symptoms of a stuck open (EGR) valve include, rough idle and stalling.
Cold Start Injector

Some vehicle models use a cold start injector. It operates as a regular injector, but only works when the engine is cold. The injector may have its own thermo switch, or may be commanded by the system control module. If either the switch or the computer circuit fails, you may have a hard time starting the engine, when cold.
Also, For a Engine Cranks But No Start Problem, Consider Checking The Exhaust System.
Engine exhaust must be able to be relieved from the engine to allow it to run. If there is an obstruction, such as a catalytic converter that has broken and plugged the exhaust system. Then, no exhaust gasses will be able to exit the engine.
(MAP) Sensor

The (MAP) sensor, is used by the (PCM) for engine load input. The (PCM) uses this input, as well as others. Consequently, to calculate the correct amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders. The (MAP) sensor, compares the barometric (atmospheric) pressure to the intake manifold vacuum. So, when the sensor fails, it can prevent your engine from starting.
(MAF) Sensor
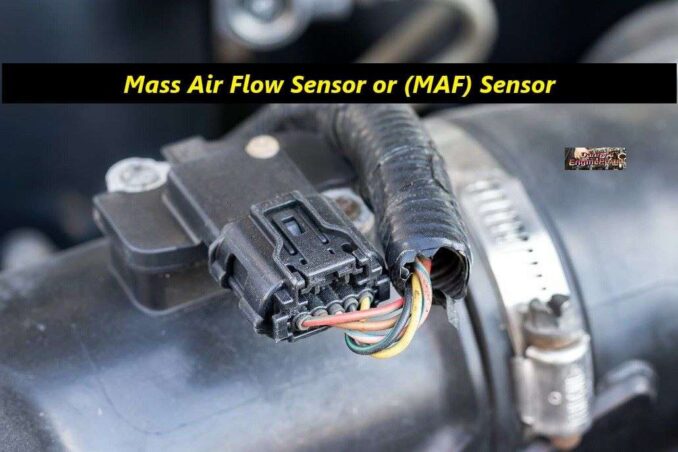

The (MAF) sensor tells the computer, the amount (the density) of the air entering the engine. A common (MAF) problem is dirt or foreign matter blocking the sensing element. As a result, stopping the sensor from working. Or, the sensor itself may fail after miles of service. You may be able to clean and test the sensor at home.
(ECT) Sensor

The computer uses the (ECT) sensor, to know how much fuel the engine needs. Also, when to enter closed loop operation. (that is, when the engine has reached operating temperature). A bad (ECT) sensor can upset ignition timing, or the operation of the transmission or cooling fan.
Canister Purge Valve

The canister purge valve, is part of the (EVAP) system. The (EVAP) system temporarily stores harmful fuel vapors into a canister, to prevent their release into the atmosphere. When conditions are appropriate, the computer routes the fuel vapors out of the canister, through a canister purge valve. And, into the intake manifold for burning. A faulty valve, though, can cause a rough running engine, and even prevent the engine from starting.
(TPS) Sensor, Engine Cranks But No Start

The (TPS) sensor monitors the position of the throttle valve. It sends a voltage signal to the computer. The computer uses this information, to regulate the air/fuel mixture according to engine needs. On some vehicle models, a worn out, failing or bad (TPS) sensor will prevent your engine from starting at all.
Vacuum Leaks
So, vacuum leaks are common. And, they are the source of many engine performance problems. Depending on where the fault is located, vacuum leaks can be hard to find.
But, major vacuum leaks that can make the engine hard to start, may happen in the:
- Power booster vacuum hose
- (EGR) valve
- Blown head
- Leaking intake manifold gasket
Carburetor

If you have an old vehicle model with a carburetor, double check that the fuel level is properly adjusted. If the carburetor is flooded, you’ll probably perceive a strong fuel odor under the hood. A little trick you can use is to fully depress the gas pedal, and try to start the engine. Finally, if the engine doesn’t start, wait for a few minutes, and try again.
Conclusion
When your engine cranks but no start, it can be difficult to fix if you don’t know where to begin. This guide not only tells you where to start, but helps you build your diagnostic strategy. And, reminds you of some simple, but easy to forget places to check into. So, most of the time, using just this guide you’ll be able to zero in on the problem.
BY DANNY BENDER




