“Choose Your (PCV) System Help Topic Below”
- (PCV) System: One Of The Biggest Causes, Of Engine Oil Sludge
- (PCV) Valve: Major Problems From Lack Of Regular Maintenance
- Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) System: What Does It Do
- PCV Valve: How Does It Work, Failure Signs, How To Test It
- PCV Valve System: This Is Where Crankcase Gases Get Recycled
- Crankcase Emission Control: Understanding Blow-By Gases
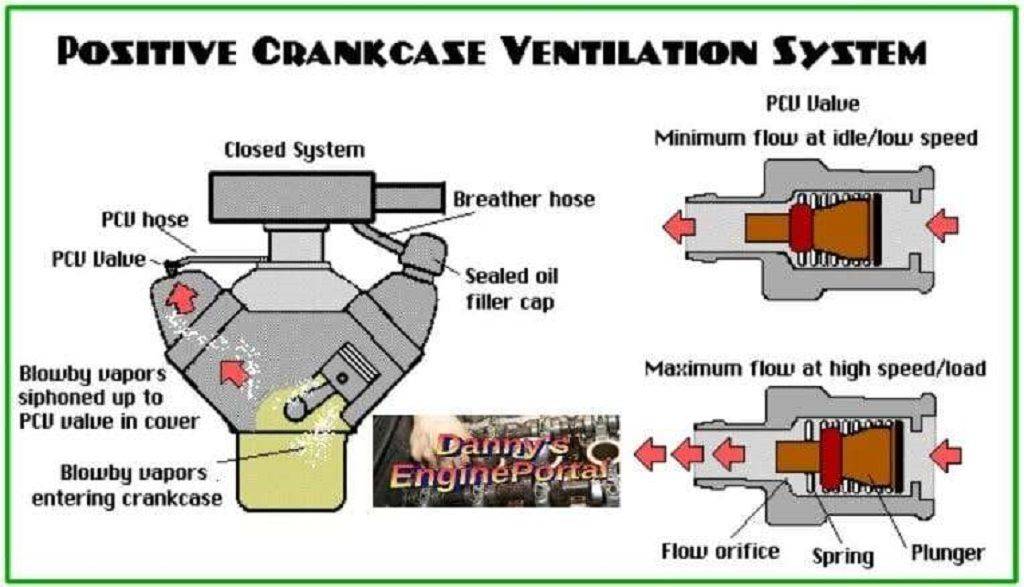
So, a (PCV) (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) system controls crankcase emissions by rerouting harmful “blow-by” gases. From the engine’s crankcase back to the intake manifold to be burned in the combustion chamber. It also manages crankcase pressure, which prevents oil leaks from seals and gaskets and reduces oil dilution. Also, prevents sludge and carbon buildup, leading to better engine efficiency, performance, and longevity.
So, How Does It Work
Blow-by gases:
During combustion, small amounts of unburnt fuel and exhaust gases leak past the piston rings into the crankcase. These are called “blow-by” gases.
Pressure buildup:
So, without a way to vent these gases, pressure builds up in the crankcase.
(PCV) action:
The PCV system uses the vacuum from the engine’s intake manifold to draw these gases out of the crankcase. Then, reroute them back into the intake manifold.
Regulation:
A (PCV) valve regulates the flow of these gases, to ensure the correct amount is reintroduced to the intake for proper combustion. And also, to avoid creating an undesirable vacuum in the crankcase.
Thank You !!
